“The best thing about being an architect is that you use both sides of the brain, the analytical – and the creative side….” RF.In order to do good work as a IT-architect, you need to be well rounded. In this page will help you to understand why It-architecture is important, what it is and my view on it.
IT-architecture why? IT-architecture movements are helping to push up the quality of the software systems that builds. IT-architecture are helping us to understanding how to set goals and plans to better software that better meets the needs of the business while carefully managing time and budgetary constraints.
Do your implementation match with your IT-architecture paradigm? If not, you have to change one of them!
A lack of IT-architecture causes problems since IT-architecture is about structure and vision, you could say that IT-architecture exists anyway.. It’s easy to see how not thinking about IT-architecture ( “bigger picture”) can lead to a number of common problems that face on a regular basis. Ask the following questions:
- Does your software system have a well-defined structure?
- What is your design philosophy?
- Is it easy to make changes in your systems?
- Do teams implement features in a consistent way?
- Is the business needs driving your system?
- Do quality level of quality congruence with vision?
- Is there a shared vision for how the software will be built across the team?
- Do team have the necessary amount of technical guidance?
- Do technical leadership exist?
- Do teams have control on Roadmap?
It is possible to successfully deliver a software project by answering “no” to some of these questions, but it does require a very good team and a lot of luck if it exists.
I have seen when nobody thinks about IT-architecture. The end result is something that looks like a big ball of spaghetti architecture. It has a structure, but it’s not one that you’d want to work with! Other side effects could include the software system being too complex, slow, expensive, insecure, fragile, unstable, hard to deploy, hard to maintain, hard to change, hard to extend, etc. I’m sure you’ve never seen or worked on software projects like this, right? Since IT-architecture is inherent in every software system, why don’t we simply acknowledge this and place some focus on it?
Be in complexity and meet the needs of the business is why we have IT-architecture.
What is IT-architecture? I think there is many definition, maybe every prominent IT-architect have their own definition of it. To no mention also different type of IT-architectsI have done research and read many books on the topic.Here is a list some of the interesting definitions and the types architecture below:
- IT-architecture is the art and science of designing and delivering valuable technology strategy. From Iasa Definition
- It’s the driver behind “many of the ideas that architects use every day: Frameworks, brokers, layers, interfaces, messaging, connectors … it’s all about the gaps! […] The architecture is the glue that binds the work of software designers together into a resilient, flexible, scalable, and ultimately useful system. From Eoin Woods reflected on this question for quite a while and found an answer.
- Software architecture is the defining and structuring of a solution that meets technical and operational requirements. Software architecture optimizes attributes involving a series of decisions, such as security, performance and manageability. These decisions ultimately impact application quality, maintenance, performance and overall success” .techopedia.com/.
- Systems Architecture is defined by the recommended practice as the fundamental organization of a system, embodied in its components, their relationships to each other and the environment, and the principles governing its design and evolution. from ANSI/IEEE Std 1471-2000.
- Recommended Practice for Architectural Description of SoftwareIntensive.
- The software architecture of a program or computing system is the structure or structures of the system, which comprise software elements, the externally visible properties of those elements, and the relationships among them. From the book Software Architecture in Practice (2nd edition), Bass, Clements, Kazman; AddisonWesley 2003.
- The set of structures needed to reason about the system, which comprises software elements, relations among them and properties of both. From the book Documenting Software Architectures: Views and Beyond (2nd Edition), Clements et al, AddisonWesley, 2010.
- Rational Unified Process, 1999 An architecture is the set of significant decisions about the organization of a software system, the selection of the structural elements and their interfaces by which the system is composed.
- The architecture of a system describes its major components, their relationships (structures), and how they interact with each other. Software architecture and design include several contributory factors such as Business strategy, quality attributes, human dynamics, design, and IT environment.
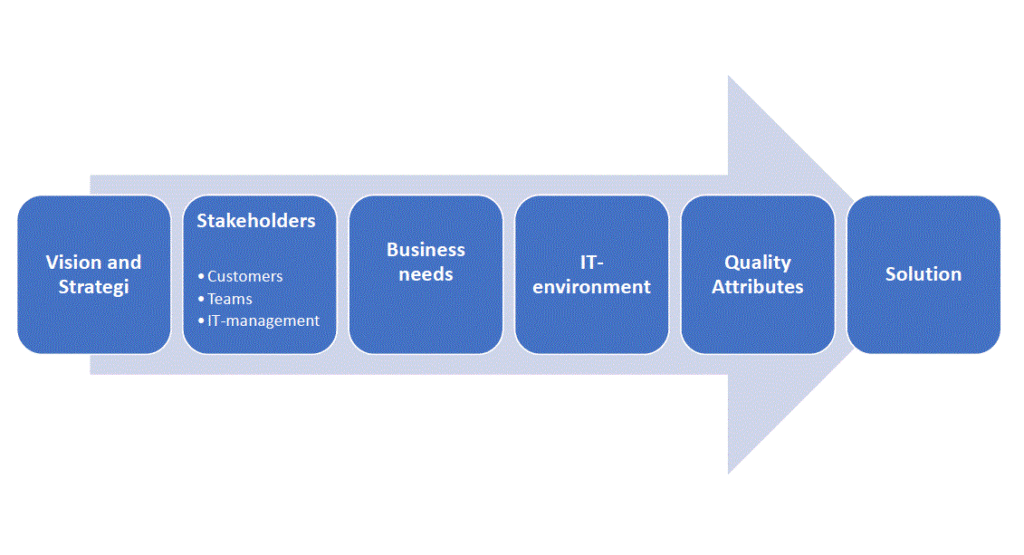
My view of the environment where an IT-architect works, we have to interact business needs, strategies, vision and major components, their relationships (structures), and how they interact with each other. IT-architecture and design include several contributory factors such as business strategy, quality attributes, human dynamics, design, and IT environment. See th picture below
The type of IT-Architect:
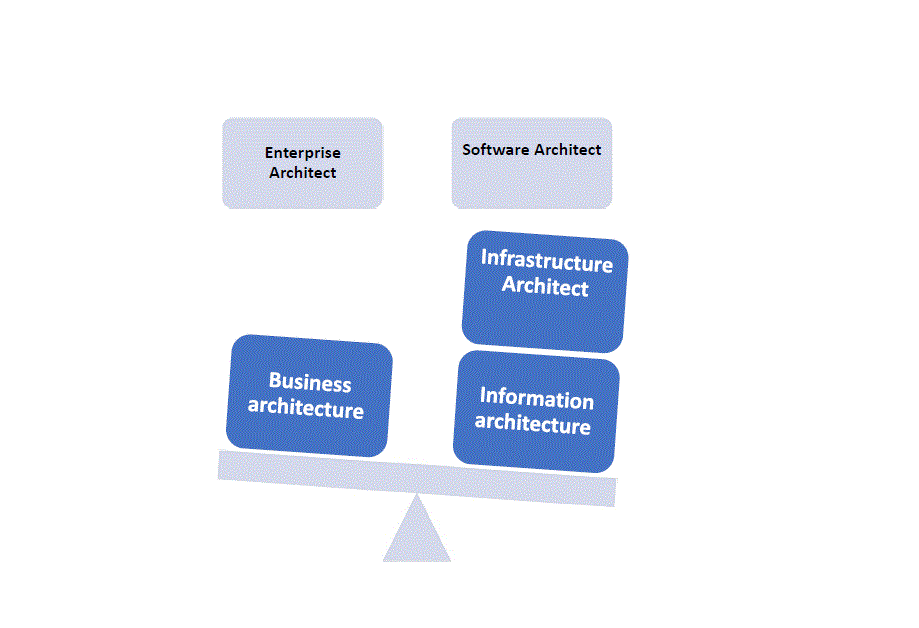
- Enterprise Architect
An enterprise architect needs to be able to understand both IT and business at a high level.
- Software Architect
They are leading technical architecture.
- Infrastructure Architect
You may have heard the term infrastructure architect bandied around and wondered.
- Business architecture − Defines the strategy of business, governance, organization, and key business processes within an enterprise and focuses on the analysis and design of business processes.
- Information architecture − Defines the logical and physical data assets and data management resources.
How to develop an IT-Architecture based on personal, communication and technical skills?
My definition may be not just be related to IT, but personal and communication skills are key to the role of an IT-architect. These two skills are particularly important given the IT-architect’s role as a leader. IT-architect’s need to be able to communicate well with superiors and subordinates. Also IT-architect needs to be a “big-picture” thinker, maybe have your own philosophy about IT-architecture. An IT-architect should be able to put their knowledge into practice and design systems in a complex landscape. Other important skill is required to document every step of their process in both technical and layman’s terms.